Persistent Data Structures
Used in Functional Programming languages for efficient implementation of immutable data structures
This is an example of a Persistent Array
Looks like an m-tree
Elements at the leaf are the actual array elements
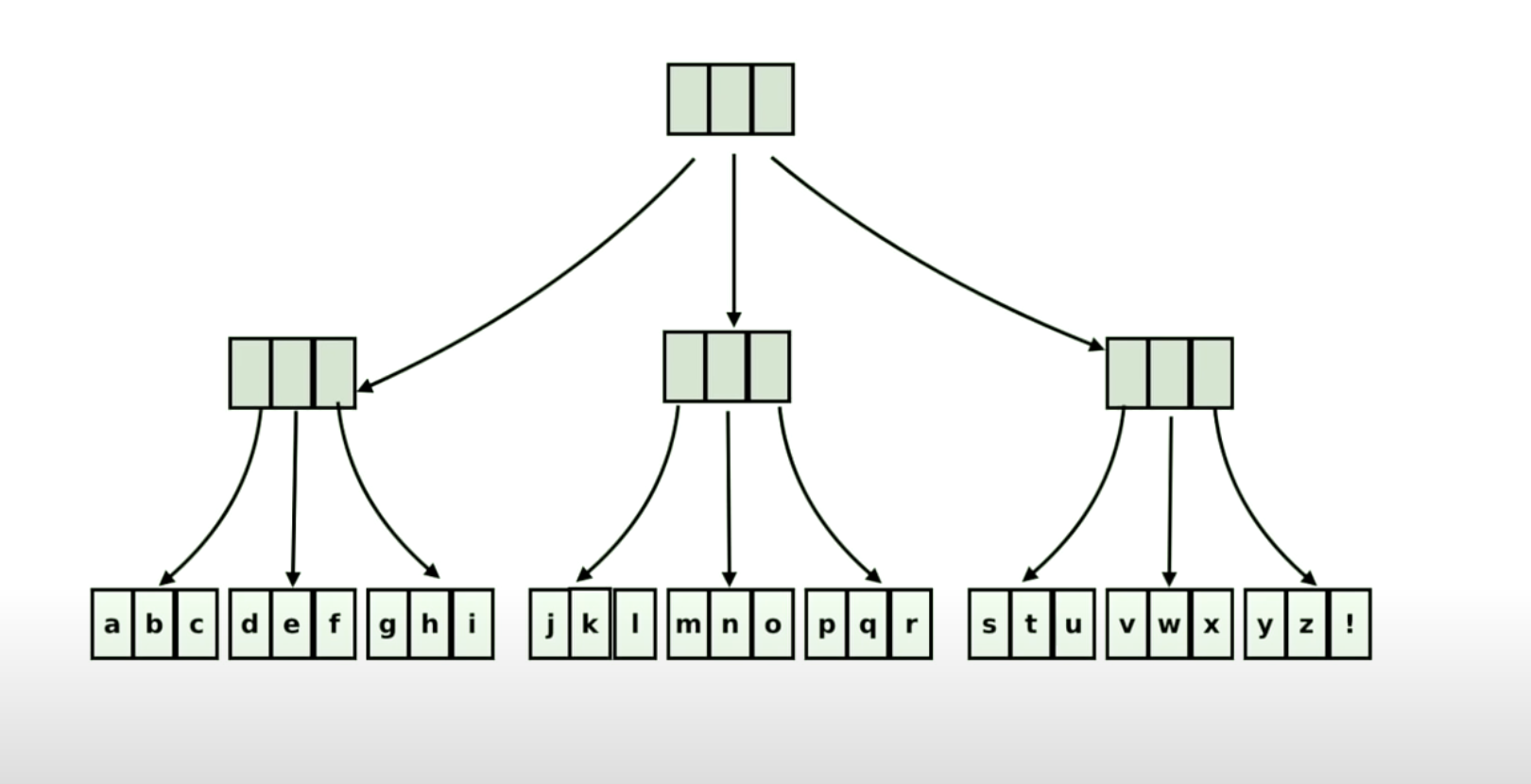
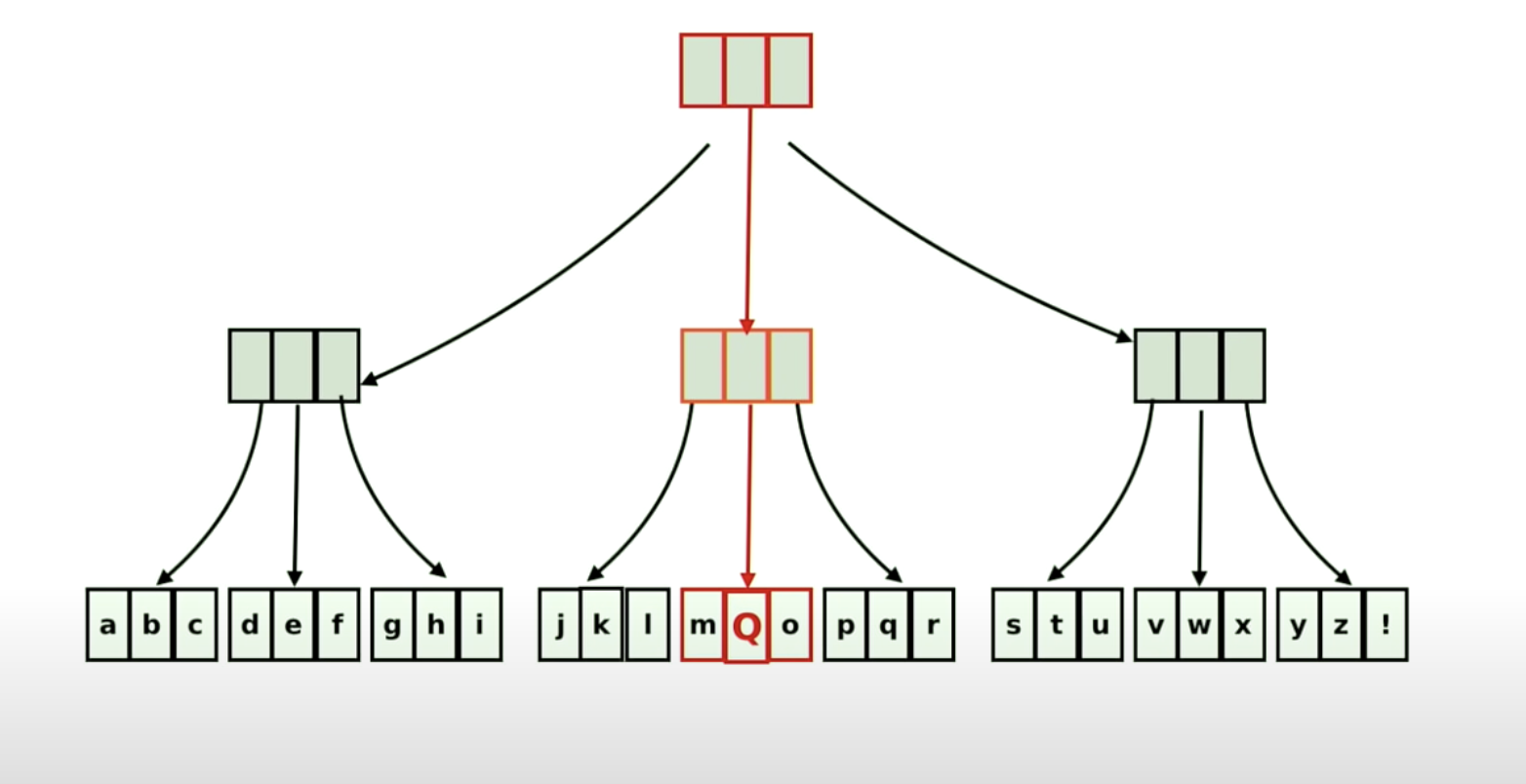
Say we want to replace n with Q.
In this case, we only need to make copies of only 3 blocks (highlighted in red), and rest of the blocks will be reused in the new variable.
In practical cases, an m-tree with 32 elements per block are used.
Calculate how many elements it can hold with just an height of 3