Processes and Threads
Program
A program is an executable file, containing instructions and some data.
Usually it is a binary executable file, or even text code in case of interpreted languages.
Processes
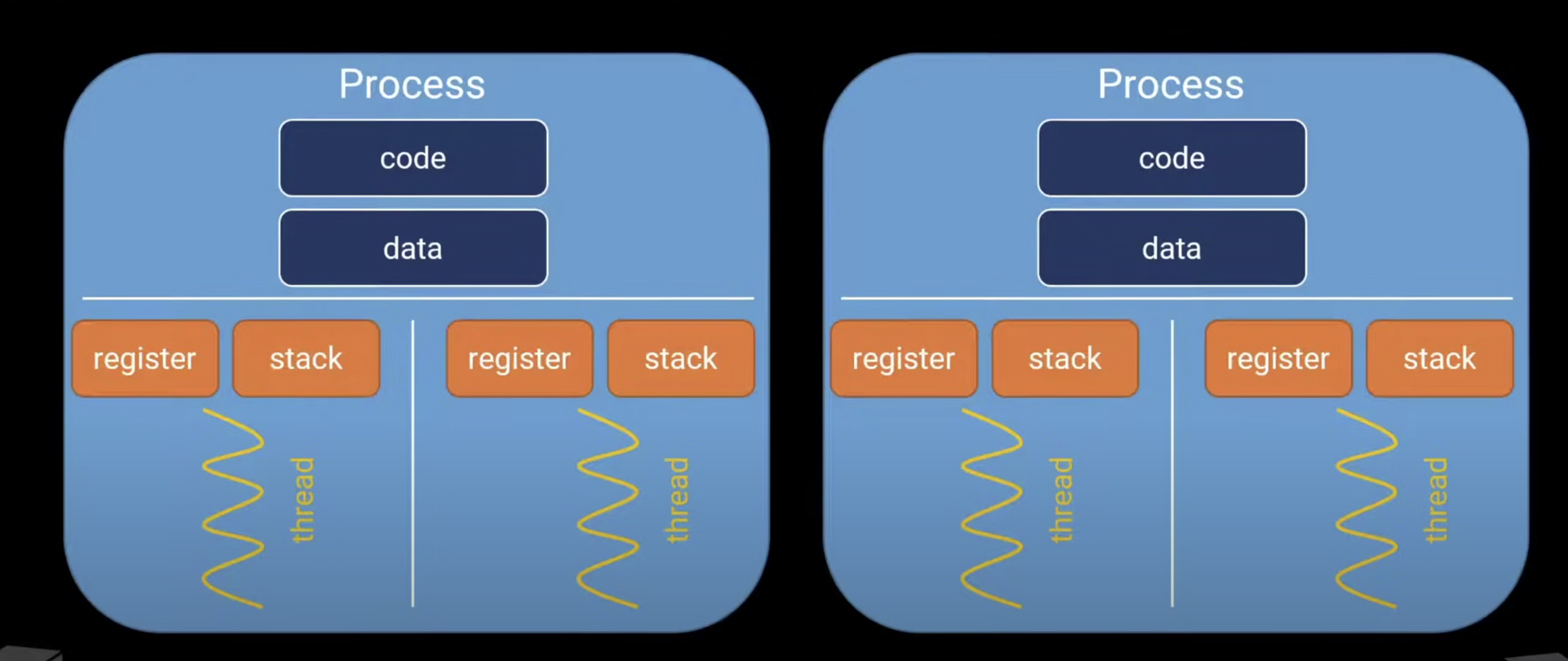
A process is an running instance of a program
Each process has its own virtual memory address space.
A process memory consists of:
- Code memory
- Data memory (global and static variables)
- Heap (for dynamic memory allocations)
- Process Stack
- Process Control Block
In Linux, a running process can spawn a new process using system calls fork(2) and execve(2)
The Linux OS keeps track of all the running processes using a Kernel Process Table
The new process has saperate virtual memory than the process that spawned it initially.
Threads
Thread is a lightweight process.
Thread is the smallest unit of a process that a can run on a CPU core.
Each process has at least 1 thread.
All the threads spawned from a process shares the virtual memory address space of the parent process.
Each thread has its own:
- Thread Stack
- Thread Control Block
Each thread shares:
- Code memory
- Data memory
- Heap
- PCB
Threads are supported by nearly all operating systems and can be created with system calls.
In Linux, a process can spawn a new thread by using system calls like clone(2) and specifying flags like CLONE_THREAD or CLONE_VM.