Intel x86-64 Architecture
Intel® Hyper-threading technology
Hyper-threading is intel’s proprietary implementation of Simultaneous multithreading (SMT)
It enables hardware level concurrent processing inside a physical CPU core.
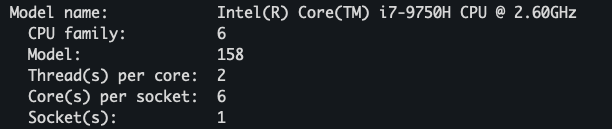
For example, the i7-9750H CPU, is taking up single socket in the motherboard.
Inside the CPU, there are 6 physical cores, which use intel’s multi-core architecture to support concurrent processing of OS threads.
Inside a physical core, if HYPER-THREADING is enabled (which is yes in above case), we can get 2 logical processors (“Threads per core” in above image) inside a physical core.
Because of HYPER_THREADING, when we run htop command, we can see see 12 individual compute units instead of 6

How does it look internally?
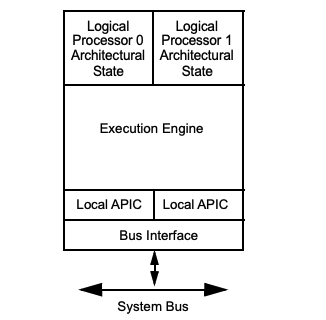
Each logical processor inside a physical core has its own Architectural State. The state contains registers. Some of them are duplicated for each processor (general purpose, xmm / ymm / zmm, segment registers), some are shared (Memory type range registers (MTRRs)), while some are shared or duplicated based on implementation.
Each logical processor has its own APIC ID, which enables OS to treat every logical processor as a seperate execution unit.
The core of the physical processor, i.e. execution unit AND the system bus is shared between logical processors
CPU cache is shared
Multi-core Architecture
In this, each processor core has dedicated microarchitectural resources identical to a single-processor implementation of the underlying microarchitecture without hardware multi-threading capability.
In Intel, each logical processor inside a dual-core processor (whether supporting Intel Hyper-Threading Technology or not) has its own APIC functionality, PAT, machine check architecture, debug registers and extensions.
Each logical processor handles serialization instructions or self-modifying code on its own. Memory order is handled the same way as in Intel Hyper-Threading Technology
The topology of the cache hierarchy (with respect to whether a given cache level is shared by one or more processor cores or by all logical processors in the physical package) depends on the processor implementation.
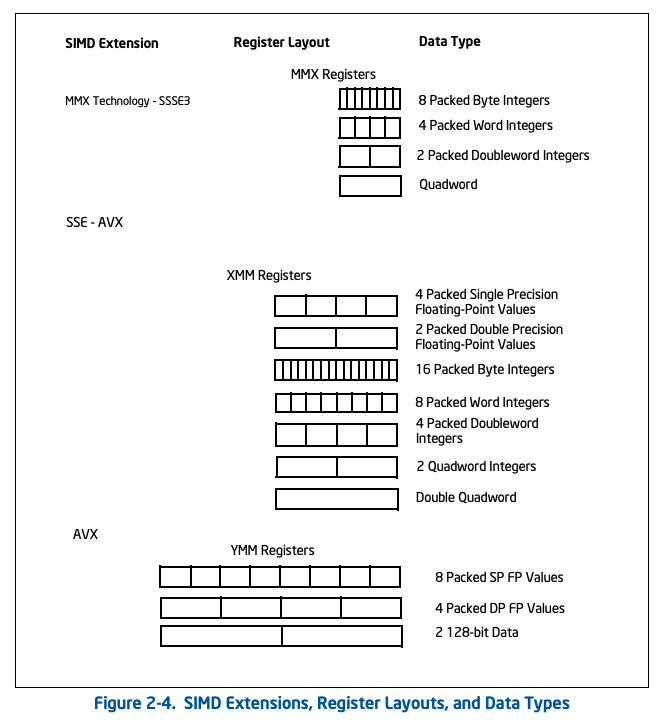
SIMD Support
Each logical processor has its own set of 8 / 16 SIMD registers
References
- Intel Architecture Developer’s Manual, volume 1 and volume 3A
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyper-threading